NANOvsCSC Optimisation of functional NANOparticles as a novel, minimal-invasive and efficient therapy for targeting Cancer Stem Cell
Dr. Francisco Terán
-
Funding : Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación. MAT2010-21822-C02-01
-
Duration: 2011 - 2012
-
24 months
The aim of the project is to investigate the dynamical magnetic properties of ferrite magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) for their therapeutic use –based on magnetic heating–against cancer cells. The MNP magnetic heating capability is currently being clinically tested as a novel treatment modality for solid cancers with promising early results. The MNP heating capabilities originate from a hysteretic non-reversible magnetic behaviour expected at dynamic regime. However, systematic studies of the dynamical MNP magnetic properties to identify the onset of hysteresis of MNP and to characterise their dynamically-induced heating capabilities are still lacking. This project has evaluated the dynamical magnetic properties and heating power in magnemite MNP as a function of size and AC magnetic field sweeping rate. Thus, the project has allowed to improve the chemical reaction conditions for synthesizing magnetite nanopartibles by thermal decomposition in organic media with optimal magnetic and magneto-thermal properties.
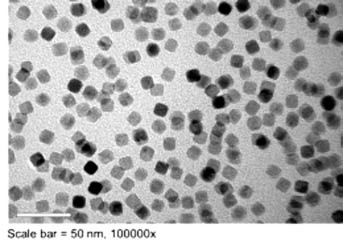
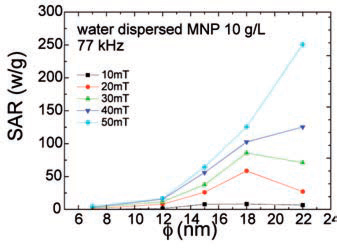
Left: TEM micrographs from 15 nm size MNP. Notice the high size uniformity. Right. SAR values of SPION measured in water dispersion at iron concentration of 10mg/ml for different sizes and magnetic field amplitudes ranging from 0 to 50 mT at a given frequency (77 kHz).
http://nanociencia.imdea.org/images/nanociencia/scientific_reports/Scientific-Report-2012.pdf#page=85




